We propose a versatile scheme to slow supersonically cooled molecules using a decelerating potential well, obtained by steering a focusing laser beam onto a pair of spinning reflective mirrors under a high-speed brake. The longitudinal motion of molecules in the moving red-detuned light field is analyzed and their corresponding phase-space stability is investigated. Trajectories of CH4 molecules under the influence of the potential well are simulated using the Monte Carlo method. For instance, with a laser beam of power 20 kW focused onto a spot of waist radius 40–100 μm, corresponding to a peak laser intensity on the order of∼108W/cm2, a CH4molecule of∼250m/s can be decelerated to∼10m/s over a distance of a few centimeters on a time scale of hundreds ofmicroseconds.
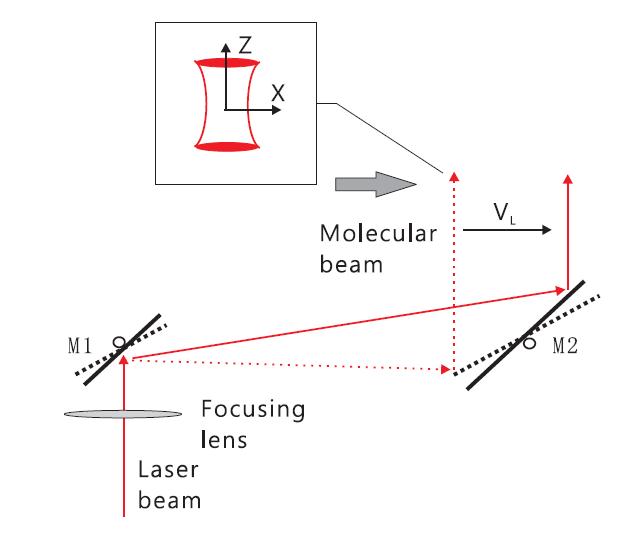
FIG. 1. Schematic diagram for decelerating molecular beams using a traveling light field.
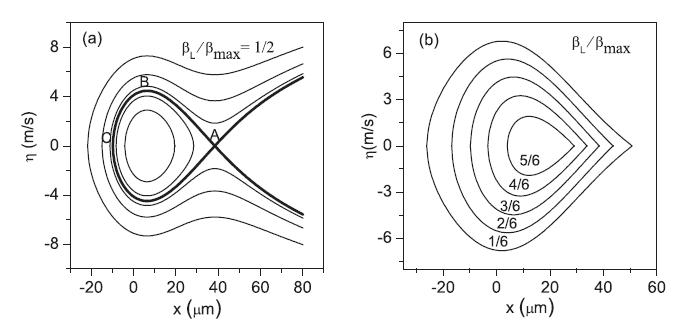
FIG. 2. (a) The trajectories of both trapped and untrapped CH4molecules in the phase space with βL = βmax/2.
(b) The phase stable areas for CH4 molecules in the decelerating potential well with βL/βmax = 1/6,2/6,3/6,4/6, and 5/6, respectively.
![]() 104、Optical Stark decelerator for molecules with a traveling potential well.pdf
104、Optical Stark decelerator for molecules with a traveling potential well.pdf

