课程信息
中法联合培养研究生项目(PRoSFER)是华东师范大学与法国巴黎-萨克雷高师、里昂高师、雷恩高师的联合办学项目,该项目于2002年11月经教育部批准正式启动,至今已运行21年,培养了大批优秀学生,得到了中法两国教育部门的高度评价,并于2016年在“中法高级别人文交流机制第三次会议”系列活动之一的中法高等教育论坛上获“中法大学合作优秀项目”奖项。
本次PRoSFER春季课程由法国国家研究中心、巴黎萨克雷大学、德州大学达拉斯分校、西安交通大学等学校在光学领域的知名教授集中授课。授课内容原子光子、自旋、量子光网络、光学非经典态等方面。课程面向华东师范大学、上海交通大学、上海理工大学、中国科学院大学等国内高校以及法国里昂大学、巴黎萨克雷大学、加拿大阿尔伯塔大学等国外高校的研究生和教师开放。授课将以线上线下相结合的授课形式进行。
授课时间
2023年5月4日—19日
授课方式
授课采用线上线下相结合的授课形式。
线下:华东师范大学闵行校区光学大楼B225会议室
线上:Zoom会议ID: 940 8915 3624,密码: 10956882
课程表
中法联合培养研究生项目(PRoSFER)2023年春季课程 | ||
第一周 | ||
5月4日 | 法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | 课程: Spin ½ 授课形式:Online |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | 课程: Spin ½ 授课形式:Online | |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
5月5日 | 法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | 课程:Two-level atom. Interaction with light 授课形式:Online |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | 课程:Two-level atom. Interaction with light 授课形式:Online | |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
第二周 | ||
5月8日 | 法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | 课程:Two-level atom. Interaction with light 授课形式:In presence |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | 课程:Two-level atom. Interaction with light 授课形式:In presence | |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
5月9日 | 法国时间:3:00-4:00am 中国时间:9:00-10:00am | 报告:Continuous-variables Quantum Optical Networks:From Generation to Application 报告形式:online |
报告人: Prof. Yin Cai Xi'an Jiaotong University | ||
法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | 课程:Introduction to noise 授课形式:In presence | |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | 课程:Introduction to noise 授课形式:In presence | |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
5月11日 | 法国时间:3:00-4:00am 中国时间:9:00-10:00am | 课程:Introduction to spin noise experiments 授课形式:In presence |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:4:15-5:15am 中国时间:10:15-11:15am | 课程:Introduction to spin noise experiments 授课形式:In presence | |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | Presentation and discussion | |
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | Presentation and discussion | |
5月12日 | 法国时间:3:00-4:00am 中国时间:9:00-10:00am | 课程:Gaussian noises and beyond 授课形式:In presence |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:4:15-5:15am 中国时间:10:15-11:15am | 课程:Gaussian noises and beyond 授课形式:In presence | |
授课人: Prof. Fabien Bretenaker French National Center for Research | ||
第三周 | ||
5月16日 | 法国时间:3:00-4:00am 中国时间:9:00-10:00am | 报告:Engineering, Characterization, and Applications of Optical Non-classical States 报告形式:Online |
报告人: Prof. Zhongzhong Qin University of Texas at Dallas | ||
法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | 课程: Spin 1 授课形式:Online | |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | 课程: Spin 1 授课形式:Online | |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
5月19日 5月19日 | 法国时间:9:30-10:30am 中国时间:15:30-16:30pm | 课程: SNS for a spin 1 system 授课形式:Online |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
课间休息(15 min) | ||
法国时间:10:45-11:45am 中国时间:16:45-17:45pm | 课程: SNS for a spin 1 system 授课形式:Online | |
授课人:Prof. Fabienne Goldfarb Paris-Saclay University | ||
授课老师介绍
Fabien Bretenaker教授 | 法国国家研究中心(French National Center for Research) |
巴黎萨克雷大学(Paris-Saclay University) | |
德州大学达拉斯分校(University of Texas at Dallas) | |
西安交通大学(Xi'an Jiaotong University) |
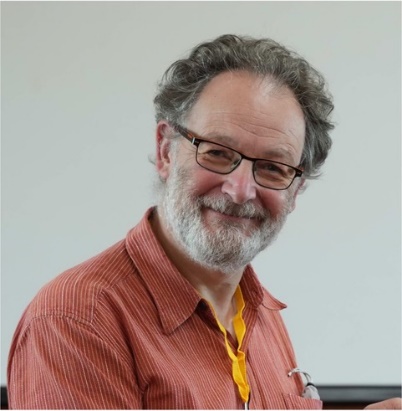

Fabien Bretenaker is a senior researcher for the French National Center for Research (CNRS) and an adjunct professor at Ecole Normale Paris-Saclay. He is currently the head of the laboratory LuMIn in Paris-Saclay University. His PhD was about gyrolasers and laser physics. He is still working in these areas but also extended his activities on atomic physics, optical information processing and quantum technologies.
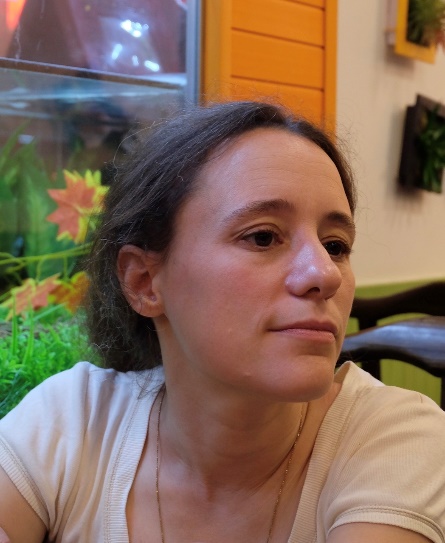

Fabienne Goldfarb is a professor in Paris-Saclay University, where she is currently deputy director of the Institute of the Sciences of Light. She made her PhD on electronic matter waves, and a post-doc in Austria on molecular matter waves. She now focuses more on atomic physics and light-matter interaction, with possible applications for quantum technologies.

Zhongzhong Qin received his Bachelor degree from Shanxi University in 2010. After receiving his PhD degree from East China Normal University in 2015, he accepted the position of Assistant Professor at Shanxi University, and then was promoted to Professor in 2021. In November 2022, he joined the University of Texas at Dallas as a Research Associate. His research interests lie broadly in the areas of quantum optics, quantum information and optical neural network. He has more than 30 peer-reviewed papers and around 800 total citations. Some of his works are published in prestigious journals, including Physical Review Letters, Science Advances, and PNAS.
In 2016, Dr. Yin Cai obtained the PhD diploma from the LKB laboratory of ENS,Paris. Now he is a professor in Xi’an Jiaotong University. His research focuses on the quantum optics and quantum information, and in particular, he did systematic works in constructing quantum networks using frequency comb and atomic nonlinearity. Recently, he has two projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China, and publications in the journals of Nature Communications, Physical Review Letters, etc.
课程信息介绍
Lecture: Atoms, spins and photons: From basis to spin noise spectroscopy
Fabien Bretenaker and Fabienne Goldfarb
When Alexandrov and Zapasskii demonstrated for the first time that the Faraday rotation noise spectrum can be used to detect magnetic resonances [AZ1981], the experiment was a real feat. More than 20 years later, thanks to technical advances in lasers, detection and signal processing tools, this method was rediscovered for studying spin dynamics in atoms as well as in solid-state paramagnets.
In this lecture, we progressively introduce the tools necessary to understand what is spin noise spectroscopy. We begin with the spin ½ and the two-level atom interacting with light, before giving some theoretical and practical background about noise. We will end up with recent spin noise spectroscopy results obtained with spin 1 atoms.
[AZ1981] E.B.Aleksandrov,and V.S.Zapasskii, JETP54, 64 (1981)
Seminar: Engineering, Characterization, and Applications of
Optical Non-classical States
Zhongzhong Qin
Research Associate, University of Texas at Dallas
Optical non-classical states, which include squeezed state, entangled state, single photon state, and Schrödinger cat state, are the cornerstone of quantum mechanics and quantum information science. In this talk, I will introduce the fundamental principles and experimental progresses on the generation, characterization and applications of various optical non-classical states. I will focus on two commonly used methods for the generation of optical non-classical states, namely four-wave mixing in atomic vapor and optical parametric oscillator based on nonlinear crystal. Furthermore, I will introduce our recent work on the generation and manipulation of squeezed Schrödinger cat state via an all-optical in-line squeezer.
Seminar: Continuous-variables Quantum Optical Networks:
From Generation to Application
Yin Cai
Multimode squeezing and entanglement are essential for constructing quantum networks and realizing quantum information processing. Based on the optical frequency combs, we will introduce some recent advances in building reconfigurable graph states and multi-parameter estimation. Also, with such method, some new quantum sates and applications for EPR steering and CVQKD will be discussed. In addition, using atomic coherence and nonlinearity, we will also present some new results of quantum entanglement with multimode and non-Hermitian control.